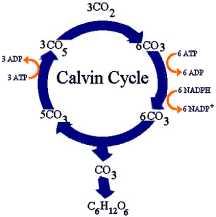
- Calvin cycle produces sugar and other organic compounds used as fuel
- Starting material is regenerated each cycle
- Starting material is RuBP, a sugar with five carbons
- Inputs of cycle: carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH
- Outputs: small energy-rich sugar molecule called G3P
- G3P: Raw material to make glucose and other organic molecules
- Light reactions take place in thylakoid membranes
- Convert light energy to chemical energy of ATP and NADPH
- Light reactions use water in equation and produce oxygen
- Calvin cycle takes place in stroma
- Uses ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into sugar
- Photosynhesis is first step in flow of energy through ecosystem
- Chemical energy passed from producers to consumers
- Photosynthesis is ultimate source of food and oxygen
Concept Check 8.3
1) What are the inputs and outputs of the Calvin cycle?
The inputs are carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH. The output is G3P.
2) Which stage of photosynthesis uses each reactant from the overall photosynthesis equation? Which stage generates each product from the overall photosynthesis equation?
The light reactions use water as a reactant and produce oxygen. The Calvin cycle uses carbon dioxide as a reactant and produces sugar.
3) Why is the Calvin cycle called a cycle?
The Calvin cycle is a cycle because the starting material, RuBP, is regenerated.
4) What molecule is the direct product of photosynthesis? How is that molecule then used by plant cells?
The direct product of photosynthesis is a small sugar molecule called G3P. With G3P, plant cells can make glucose or any other organic molecule it needs.

No comments:
Post a Comment